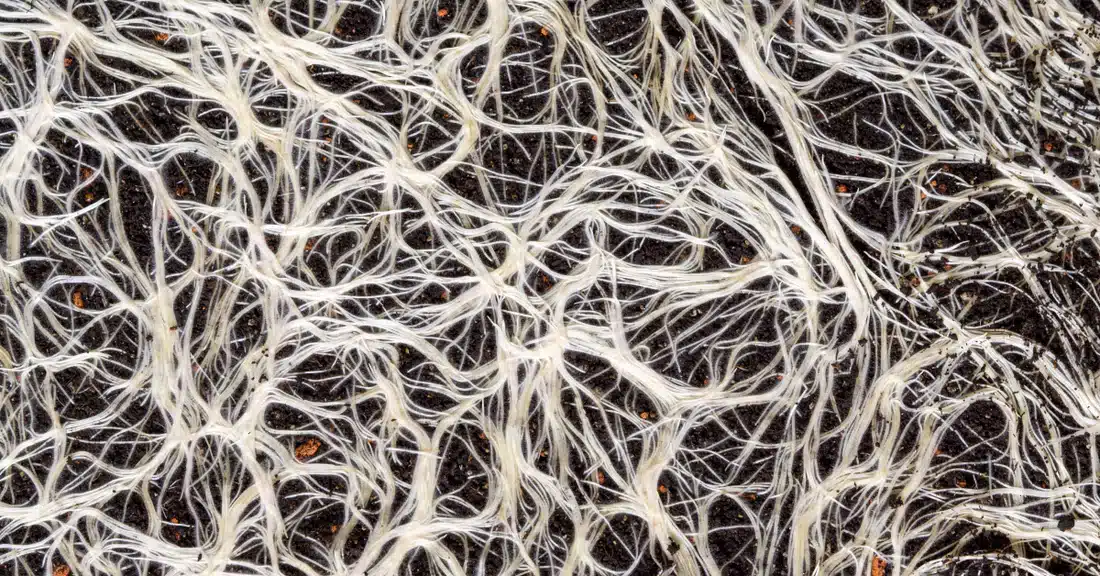
Mycelium, often unnoticed beneath our feet, is a remarkable component of the fungal world, fundamental to the health and balance of ecosystems. This complex, thread-like network serves as the lifeblood of fungi, facilitating nutrient absorption and growth. Beyond its ecological role, mycelium offers significant benefits to human health, providing essential compounds that boost immunity, protect against disease, and potentially enhance mental well-being. This introduction delves into the intricate world of mycelium, revealing its critical functions and the profound impact it has on our environment and health.
Quick Summary
- Mycelium’s Role: Fundamental in fungal lifecycle and ecosystem nutrient cycling.
- Health Benefits: Offers bioactive compounds beneficial for health.
- Sustainable Uses: Employed in innovative sustainable technologies.
- Environmental Impact: Crucial for maintaining ecosystem balance.
What is Mycelium?
Mycelium is the vegetative part of a fungus, consisting primarily of a network of hyphae. These hyphae are thread-like structures that extend into the environment, absorbing nutrients and water, essential for fungal growth. This vast, often unseen network works much like the roots of a plant, anchoring the fungus while facilitating the uptake of sustenance through its extensive reach.
The growth of mycelium is a critical phase in the life cycle of fungi, allowing them to reproduce and spread. It forms the foundation for the development of fungal fruiting bodies, which are often visible as mushrooms. The adaptability of mycelium is notable; it can thrive in diverse environments, from wood and soil to plant surfaces and animal bodies, exhibiting incredible resilience and versatility.
In addition to its ecological role, mycelium is known for its potential health benefits. It contains a variety of bioactive compounds that have been studied for their immune-modulating properties. Research suggests that these compounds can enhance immune function, reduce inflammation, and support overall health. For a deeper understanding of how mycelium contributes to health, consider exploring articles that detail its bioactive components and their effects, such as those found in medical databases and health-focused publications.
By studying mycelium, researchers continue to uncover its vast potential, from ecological contributions to promising health benefits, highlighting its importance in both natural and clinical settings.
Health Benefits of Mycelium
Mycelium is renowned for its broad spectrum of health benefits, as supported by rigorous scientific research. Here is an expanded breakdown of its benefits:
Enhanced Immune Function: Beta-glucans present in mycelium are vital for boosting immune efficiency. They function by activating macrophages and natural killer cells, which are crucial for detecting and destroying pathogens. This immune-enhancing property is thoroughly detailed in studies published in the Journal of Immunology.
Antioxidant Capabilities: Mycelium’s antioxidants play a crucial role in reducing oxidative stress, a precursor to several chronic diseases including cancer and cardiovascular disorders. These antioxidants help in neutralizing free radicals, thereby protecting cells from damage. This benefit is highlighted in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Support for Mental Health and Cognitive Functions: Research suggests that mycelium can significantly support brain health. Its contributions to neurogenesis and neuroprotection are vital for improving cognitive functions and potentially mitigating the effects of neurodegenerative diseases.
Each of these benefits is underpinned by extensive scientific research, providing a solid foundation for the therapeutic use of mycelium. For a deeper exploration of how these compounds interact biologically to promote health, detailed articles and studies can be found in the respective journals mentioned.
Mycelium in Sustainable Practices
Mycelium is gaining attention for its potential in sustainable practices, such as creating biodegradable packaging materials and other eco-friendly products. These innovations are crucial for reducing waste and promoting environmental sustainability, showcasing mycelium’s role beyond the natural world.
The Ecological Impact of Mycelium
Mycelium significantly affects nutrient dynamics within soil ecosystems. It decomposes organic compounds, which enriches soil fertility and supports plant growth. Additionally, mycelium forms symbiotic associations with plant roots, enhancing water and nutrient absorption, thus supporting plant health and soil quality.
Conclusion
Mycelium, with its intricate underground network and vast array of benefits, underscores the profound connection between nature and human health. This foundational fungal network not only enriches our ecosystems but also offers promising advantages for our physical and mental wellbeing. As we continue to unearth more about mycelium’s capabilities, it becomes clear that this remarkable organism has much to contribute to both environmental sustainability and healthcare innovations. Embracing the full scope of mycelium’s potential can lead us towards healthier lives and a more sustainable world.
Why Try Products Utilizing Mycelium?
Mycelium-based products offer sustainable alternatives to conventional materials, contributing to a healthier ecosystem. Trying these products can be a step towards supporting environmentally friendly practices and benefiting from natural, potent biological ingredients.
For a detailed exploration of the topic, consider looking into scientific studies and additional resources that delve into the specifics of mycelium’s benefits and applications.
References:
- Jo, Charles, et al. “Unlocking the Magic in Mycelium: Using Synthetic Biology to Optimize Filamentous Fungi for Biomanufacturing and Sustainability.” Materials Today Bio, vol. 19, Apr. 2023, p. 100560, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100560.
- Mirończuk-Chodakowska, Iwona, et al. “Beta-Glucans from Fungi: Biological and Health-Promoting Potential in the COVID-19 Pandemic Era.” Nutrients, vol. 13, no. 11, 6 Nov. 2021, p. 3960, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113960.
- Rai, Sachchida Nand, et al. “Therapeutic Applications of Mushrooms and Their Biomolecules along with a Glimpse of in Silico Approach in Neurodegenerative Diseases.” Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie, vol. 137, 1 May 2021, p. 111377, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33601145/, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111377.
- Vamanu, Emanuel. “Antioxidant Properties of Mushroom Mycelia Obtained by Batch Cultivation and Tocopherol Content Affected by Extraction Procedures.” BioMed Research International, vol. 2014, 2014, pp. 1–8, https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/974804.